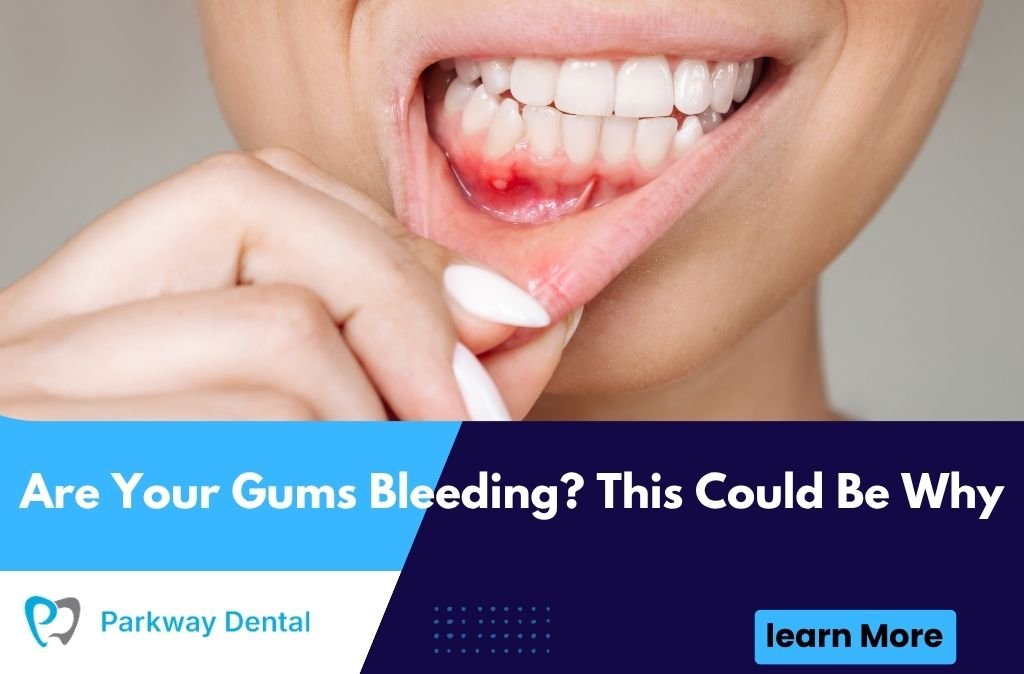
Bleeding gums aren’t just unpleasant—they may signal important oral health issues. From gum disease to vitamin deficiencies, identifying the cause early helps prevent more serious problems like tooth loss or infection.
Common Causes of Bleeding Gums
Exploring the root reasons why your gums bleed is the first step to healthy gums.
Gingivitis – The Early Stage of Gum Disease
Bleeding when brushing or flossing can be an early sign of gingivitis, which is inflammation caused by plaque buildup. If caught early through improved hygiene and dental cleanings, gingivitis is reversible without lasting damage.
Poor Brushing and Flossing Technique
Using a hard-bristled brush or flossing too aggressively can irritate gums. Proper technique with soft bristles and gentle flossing prevents damage while keeping gums clean and healthy.
Nutritional Deficiencies and Systemic Conditions
Gum bleeding may point to deficiencies in vitamin C or vitamin K, or systemic conditions like diabetes or blood clotting disorders. Recognizing these links helps direct appropriate treatment beyond dental hygiene alone.
Why Immediate Attention to Bleeding Gums Matters
Bleeding gums should not be ignored. Acting early can preserve your dental and overall health.
Prevention of Periodontitis and Tooth Loss
Bleeding gums may signal early gum disease. Without treatment, it can progress to periodontitis, causing loss of connective tissue and bone—eventually leading to tooth loss.
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Prevention
A dental professional can diagnose problems early through exams and x‑rays. Early treatment avoids more invasive — and costly—procedures down the line and maintains stronger long-term oral health.
Diagnosis and What to Expect During a Dental Exam
A proper diagnosis requires a professional evaluation to tailor treatment to your needs.
Visual Inspection and Gum Probing
During your dental visit, your dentist will check gum color, swelling, pocket depth, and plaque. This helps determine if gum pockets suggest rising periodontal disease or mild inflammation.
X‑rays and Imaging for Underlying Assessment
X‑rays are used to evaluate your jawbone health and detect bone loss that may not yet be visible during a visual exam, allowing precise diagnosis and treatment planning.
Effective Treatment Options for Bleeding Gums
Once a cause is identified, appropriate treatment restores gum health and prevents progression.
Professional Dental Cleanings and Scaling
Scaling removes plaque and hardened tartar from above and below the gum line to stop inflammation. Regular cleanings usually prevent gingivitis from advancing and support long-term gum health.
Advanced Periodontal Treatments and Laser Therapy
If gum disease is more advanced, deep cleaning (root planing) or newer methods like laser gum therapy may be recommended to remove infected tissue while preserving healthy gums.
Lifestyle Changes to Improve Gum Health
Daily habits directly influence how healthy your gums remain over time.
Optimal Brushing, Flossing & Oral Hygiene Habits
Brush at least twice daily, floss daily, and consider interdental brushes or water flossers for areas that are hard to reach. Rinsing with mouthwash also helps reduce bacteria.
Non-Dietary Factors: Smoking, Stress, and Medications
Smoking constricts blood flow to gums, causing poor healing. Chronic stress can weaken immunity. Certain medications, like blood thinners, can increase gum bleeding risk. Identifying these factors assists in prevention.
When Bleeding Gums May Indicate a Systemic Health Concern
Persistent bleeding gums might signal broader health issues.
Blood Disorders, Hormonal Changes, and Diabetes
Conditions like leukemia or clotting disorders may cause persistent gum bleeding. Hormonal shifts during pregnancy or menopause can increase gum sensitivity. Diabetes also impairs healing—these require medical as well as dental attention.
Oral Cancer and Unusual Gum Bleeding
While rare, unexplained gum bleeding or sores that don’t heal may signal oral cancer. Routine dental exams include checks for abnormalities that warrant further medical evaluation.
Everyday Scenarios That Can Lead to Gum Bleeding
Sometimes, the cause of bleeding gums is something you don’t expect—or a routine habit that needs a small tweak.
Brushing Too Hard or Using the Wrong Toothbrush
Using a hard-bristled toothbrush or brushing with excessive pressure can wear down gum tissue and cause bleeding. Always opt for a soft-bristle brush and brush in gentle, circular motions.
Skipping Flossing for Too Long
If you’ve gone weeks or months without flossing, gums may bleed when you start again. This is due to inflammation from built-up plaque. Continued gentle flossing usually stops bleeding within a few days.
Gum Bleeding in Children and Teenagers
Bleeding gums aren’t just an adult issue. Kids and teens can experience it too—and it needs just as much attention.
Poor Brushing Habits in Kids
Young children often brush too lightly or skip brushing altogether. This causes plaque to sit on the gum line, triggering mild gingivitis and gum irritation. Parental supervision helps encourage good brushing habits.
Orthodontic Appliances and Gum Sensitivity
Braces and other dental appliances can irritate the gums, especially if cleaning around wires isn’t thorough. Regular cleanings and water flossers help teens maintain better gum health during orthodontic treatment.
Pregnancy and Hormonal Causes of Gum Bleeding
Pregnancy, menopause, and puberty can increase gum sensitivity and bleeding, even with good hygiene.
Pregnancy Gingivitis
Hormonal changes during pregnancy increase blood flow to the gums, making them more prone to inflammation and bleeding. Routine dental checkups during pregnancy are essential to prevent complications.
Menopause and Hormonal Fluctuations
Reduced estrogen levels during menopause can lead to dry mouth and gum inflammation, which makes bleeding more likely. Dentists often recommend hydrating mouthwashes or hormone-friendly dental products.
At-Home Remedies for Managing Minor Gum Bleeding
If your gums are bleeding but you’re not in pain, there are a few ways to calm inflammation at home before your dental visit.
Saltwater Rinse
Mixing warm water with salt (½ tsp in 1 cup) creates a gentle rinse that reduces swelling and bacteria. Use it twice daily for relief from mild gum inflammation.
Hydrogen Peroxide Rinse
Diluted hydrogen peroxide (equal parts peroxide and water) can help reduce bacteria and inflammation. Use cautiously—no more than 2–3 times a week—and never swallow it.
How to Prevent Bleeding Gums with Daily Care
Good habits practiced daily can keep your gums healthy and stop bleeding before it starts.
Brush Twice a Day for 2 Minutes
Consistency matters. Brushing with a fluoride toothpaste for two minutes removes food particles and keeps plaque from forming near the gum line.
Floss Daily Without Aggression
Slide the floss gently along each tooth and curve it into a “C” shape to clean below the gum line without cutting into your gums.
Use Mouthwash to Kill Bacteria
An alcohol-free antibacterial mouthwash helps rinse away leftover bacteria and soothes irritated gums—especially after flossing.
Conclusion
If your gums are bleeding, don’t ignore the signs. Whether it’s a result of gingivitis, poor technique, or a medical condition, early care is the best care. Daily habits, professional cleanings, and routine exams all work together to keep your gums—and your smile—strong and healthy.
If you’re experiencing persistent bleeding gums or need preventive care, schedule a visit with a trusted Dentist in West Roxbury, MA. With personalized care and the latest in gum treatments, you’ll be back to smiling confidently in no time.
FAQs
What causes gums to bleed while brushing?
The most common cause is gingivitis from plaque buildup. It can also be due to brushing too hard or using the wrong toothbrush.
Are bleeding gums always a sign of gum disease?
Not always. They can also result from vitamin deficiencies, pregnancy, medications, or brushing too aggressively.
Can bleeding gums heal on their own?
With improved oral hygiene and regular cleanings, mild bleeding gums can heal. But if symptoms persist, professional treatment is needed.
What mouthwash is good for bleeding gums?
Look for alcohol-free, antibacterial mouthwashes that are formulated to fight gingivitis and support gum healing.
How can I stop my gums from bleeding naturally?
Brush gently, floss daily, and rinse with saltwater. Stay hydrated and avoid tobacco or sugar-heavy foods that irritate the gums.
Should I see a dentist if my gums bleed occasionally?
Yes. Even occasional bleeding could be an early sign of gum disease. A quick exam can prevent more serious problems later.
Is bleeding gum during pregnancy normal?
Yes, it can be. Pregnancy gingivitis is common, but it still requires dental supervision to prevent infection or gum recession.
Can children get gum disease?
Yes. Children can develop early-stage gingivitis, especially with poor brushing habits or orthodontic appliances.
Will changing my toothbrush help stop the bleeding?
Yes. Switching to a soft-bristle toothbrush and improving brushing technique can reduce irritation and bleeding.
How do dentists treat bleeding gums?
Treatment may include a professional cleaning, scaling and root planing, or laser therapy, depending on severity. Your dentist may also review hygiene techniques and check for systemic causes.